Complement of a set A, denoted by Ac, is the set of all elements that belongs to universal set but does not belong to set A. In mathematical form, complement of a set can be expressed as:
Ac = { x: x∈U and x∉A }
In simple terms,
Ac = U-A
Here, the complement of set A is computed with respect to universal set (considering set A is a subset of universal set U). This type of complement is known as absolute complement.
Complement of Set Examples
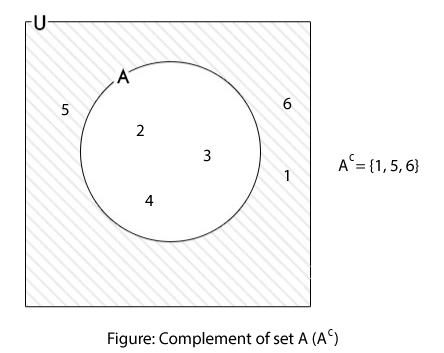
Example #1: Complement of a set with Venn Diagram
If U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} and A = {2, 3, 4}, find Ac.
Here,
U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
A = {2, 3, 4}
∴ Ac = U-A = {1, 5, 6}
Example #2
If U = { x:x is an integer} and A = { x:x is an even integer} then, find Ac.
Here,
U = { x:x is an integer}
A = { x:x is an even integer}
Now,
Ac = U - A = { x:x is an integer} - { x:x is an even integer}
∴ Ac = {x:x is an odd integer}
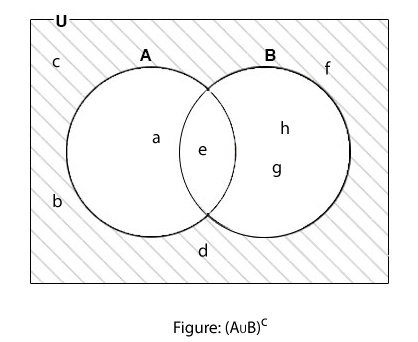
Example #3: Complement of Union of Set
If U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h} and A∪B = {a, e, g, h}, find (A∪B)c.
Here,
U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h}
A∪B = {a, e, g, h}
(A∪B)c = U - (A∪B)
∴ (A∪B)c = {b, c, d, f}